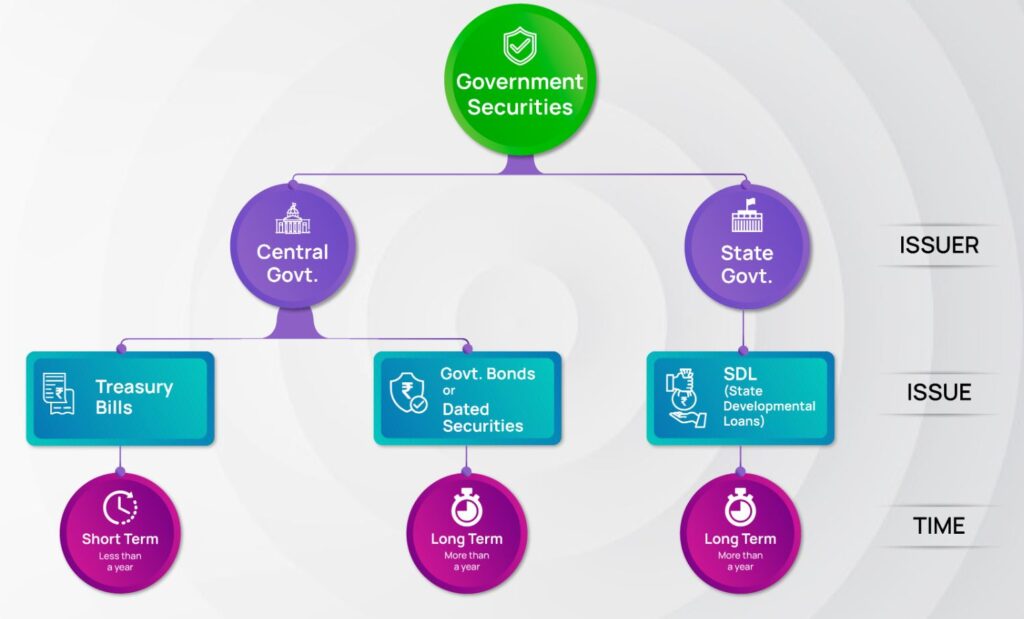
G-Sec Bonds in India are mostly long-term investment instruments with periods ranging from five to forty years. They are issued under the general category of government securities or G-Sec. The Indian government, both at the federal and state levels, may issue it. State Development Loans (SDLs) are another term for government bonds that are issued by state governments.
A government bond is a debt instrument issued by the Central and State Governments of India. When the issuing body—the federal or state governments—faces a liquidity crisis and needs money for infrastructure development, they issue these bonds.
Large investors, like corporations and commercial banks, were the target market for the majority of G-Secs when they were first issued. But gradually, the Government of India (GOI) opened up government securities to smaller investors, including co-ops and private investors.
Types Of G-Sec Bonds
Fixed-rate bonds
These kinds of government bonds have a fixed rate of interest that doesn’t change throughout the course of the investment, even if market rates fluctuate.
Floating Rate Bonds (FRBs)
As the name implies, the rate of return on Floating Rate Bonds might fluctuate over time. During the issue of these bonds, rate changes are made at predetermined periods.
SGBs, or Sovereign Gold Bonds
Sovereign Gold Bonds are issued by the Central Government, allowing entities to invest in gold for an extended period of time without having to worry about having to purchase actual gold. These bonds do not require tax on interest earned.

The cost of these bonds is correlated with the price of gold. The simple average of the closing prices of 99.99% pure gold, three days before the issuing of such bonds, is used to determine the nominal value of SGBs. Additionally, SGBs are expressed in terms of one gram of gold.
Inflation-Indexed Bonds
This particular financial instrument is one in which both the principal and the interest accrued are adjusted for inflation. These bonds, which are primarily offered to retail investors, are indexed based on either the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) or the Consumer Price Index (CPI). By guaranteeing the stability of actual returns on investments, these IIBs enable investors to protect their portfolios from inflation.
7.75% GOI Savings Bond
In 2018, this G-Sec Bond was issued to replace the 8% Savings Bond. These bonds have a 7.75% interest rate, as can be inferred from their name. RBI regulations state that the only people who can hold these bonds are
- An Individual/individuals who are not NRI in any capacity
- A minor with a legal guardian representative
- A Hindu undivided family
Zero-Coupon Bonds
As the name suggests, Zero-Coupon Bonds do not earn any interest. The difference between the redemption value (at par) and the issuance price (at a discount) is what generates earnings on zero-coupon bonds. These bonds are made using pre-existing securities rather than being offered at an auction.
How Do G-Sec Bonds Work – Explained
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues debt securities known as G-Sec Bonds in India. The proceeds from the sale of the bonds are used by the government for funding ongoing projects, specialized infrastructure, and military operations. The bond’s issuer guarantees that, in return for your investment, the principal will be repaid on a specified date. Until that day, the issuer also pays a unique G-Sec interest rate.
The most alluring part of G-Sec Bonds is the fact that their credit risk is negligible. They cannot possibly default on the repayment because they are supported by the government. Investors have the freedom to purchase and sell G-Sec Bonds on the secondary markets as they see fit.
Treasury bonds, treasury bills (T-Bills), and dated securities are a few types of government securities.
How You Can Invest In G-Sec Bonds
| RETAIL INVESTORS REGISTERED WITH NSE TRADING MEMBER | ALL RESIDENT INDIVIDUALS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Option 1: Through NSE Trading Member | Option 2: Through NSE goBID mobile app/web platform | Through NSE goBID mobile app/web platform | |
| Eligible Investors | All eligible investors as permitted by RBI | All eligible investors as permitted by RBI | Only resident individuals |
| KYC Compliance | If existing active client of NSE trading member, no additional KYC New investor should complete KYC with NSE trading member | If existing active client of NSE trading member, no additional KYC New investor should complete KYC and register as client with NSE trading member | No additional KYC if already done through any of SEBI registered intermediary New investor should complete KYC with any SEBI intermediary |
| Demat Account | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory |
| Investor Registration | No additional registration required if already having active account with NSE trading member | One time registration on NSE goBID platform | One time registration on NSE goBID platform |
| New investor registration on NSE goBID | Not applicable | Investor selects respective trading member at time of registration* Registration subject to – Respective trading member has provided valid investor records to Exchange Successful validation of investor category, demat and bank account with depositories * Available only if trading member is registered (See Point 1 below) on NSE goBID | Investor can register directly without selecting trading member of NSE Registration subject to – Valid KYC details of investor available with SEBI registered KRA including mobile number, email address, investor category Successful validation of demat and bank account with depositories |
| Undertaking by investor | Submit to trading member of NSE in format provided by NSE | Accept e-undertaking on NSE goBID and Terms & Conditions | Accept e-undertaking on NSE goBID platform and Terms & Conditions |
| Order placement | Submit offline or online through mobile app / web platform to the trading member | Submit through NSE goBID mobile app / web platform | Submit through NSE goBID mobile app / web platform |
| Bid | Only single bid per security in an auction is permitted | Only single bid per security in an auction is permitted | Only single bid per security in an auction is permitted |
| Payment and refund of funds | Payment and refund of funds through trading member | Payment and refund of funds through NSE Clearing Ltd. Mandatory to have online banking facility Funds accepted only from bank account linked to demat account (see point 2 below). | Payment and refund of funds through NSE Clearing Ltd. Mandatory to have online banking facility Funds accepted only from bank account linked to demat account (see point 2 below). |
| Credit of Securities | Directly in demat account of investor | Directly in demat account of investor | Directly in demat account of investor |
Advantages Of Investing In G-Sec Bonds
Sovereign Guarantee
When it comes to financial security and guaranteed profits, government bonds have an advantage. Since G-Secs are a formal declaration of the government’s financial commitment, they imply the obligation of the issuing governmental body to repay the debt according to the terms specified.
Inflation-adjusted
Balances held in Inflation-Indexed Bonds are adjusted against increasing average price level. In addition, the principal amount invested in Capital Indexed Bonds is inflation-adjusted. Due to the fact that investing in these funds increases the actual worth of the deposited cash, this feature gives investors a financial advantage.
Regular source of income
Interest payments on G-Sec Bonds are expected to be made to debt holders every six months by RBI regulations. It gives investors the chance to invest their unused money and make a consistent income.

Disadvantages of Investing In G-Sec Bonds
Low Income
The interest rates on other bond categories are generally lower, with the exception of the 7.75% GOI Savings Bond.
Loss of relevancy
Government bonds can become less relevant over time because they are long-term investment options with maturity terms ranging from five to forty years. This implies that, except IIBs and Capital Indexed Bonds, the value of such bonds decreases in the face of inflation.
Bidding Period of NSE
RBI conduct auction of G-sec and T- bills on a weekly basis as per the schedule below.
| Government Security | Bidding Period Starts on | Bidding Period | Auction Date at RBI | Settlement Date |
| NSE e-GSec | Ends on NSE e-GSec | |||
| T-Bills (91 day,182 day, 364 day) | (Monday) | (Tuesday) | (Wednesday) | (Thursday) |
| GoI Dated Securities | (Tuesday) | (Thursday) | (Friday) | (Monday) |
| SDL State Development Loans | (Monday) | (Monday) | (Tuesday) | (Wednesday) |
Conclusion
G-Sec Bonds in India are considered to be highly secure investment options due to the sovereign guarantee associated with them. Risk-averse investors who prefer superlative security of their investments devoid of uncertainty created present in market-linked instruments can look to invest in this type of securities. For groups without prior experience investing in stock market tools, it is a good long-term alternative.
